-40%
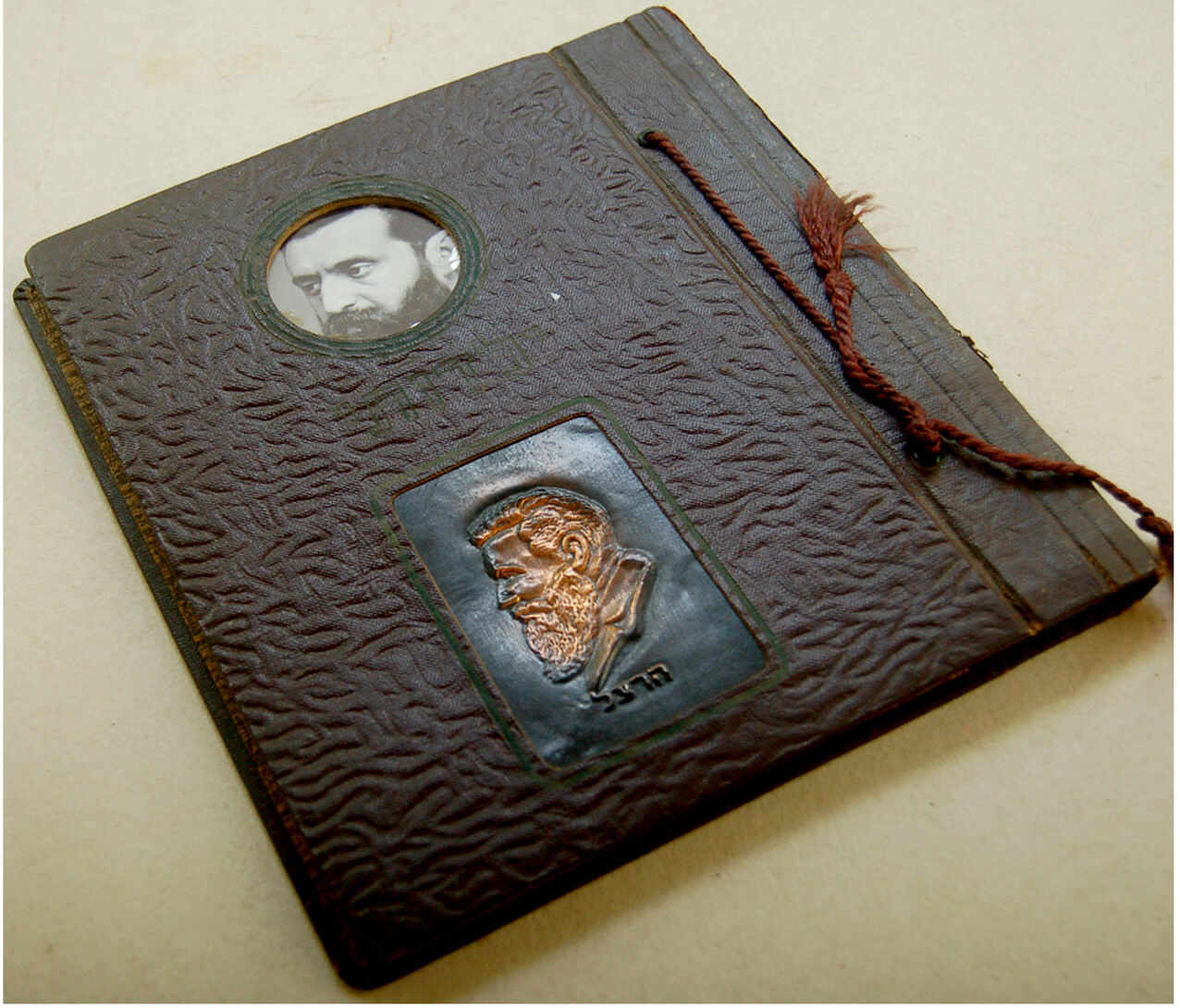
1940 Jewish HERZL COPPER PLAQUE Israel PHOTO ALBUM Judaica HEBREW Palestine
$ 42.18
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
DESCRIPTION:
Here for sale is a quite RARE and ORIGINAL vintage Judaica JEWISH-HEBREW Children PHOTO ALBUM named "YALDUTI - MY CHILDHOOD" which was published and used in the late 1940's in Eretz Israel - Palestine to store and display CHILDRENS' PHOTOS . Carries the TAX LABEL of the period. Inspite its being a familly artifact , It was designed with a VERY IMPRESSIVE image of HERZL , Being a Bezalel type COPPER ( Or brass ) PLAQUE.
HC bound with thread. 8.5 x 10". Very good condition. Unused. Empty ( No photos ). Clean black cardboard leaves with intact transparent tissue paper betweeen each two leaves. Perfectly clean. Can be used for photos. Spine wear.
( Please watch the scan for a reliable AS IS scan )
. W
ill be sent in a special protective rigid sealed packaging.
PAYMENTS
:
Payment method accepted : PAYPAL
& All credit cards
.
SHIPPING
:
Shipp worldwide via registered airmail is $ 25 .
W
ill be sent in a special protective rigid sealed packaging.
Handling around 5 days after payment.
Theodor Herzl (Hebrew: בנימין זאב הרצל (Binyamin Ze'ev Herzl)) (May 2, 1860–July 3, 1904) was an Austrian Jewish journalist who founded modern political Zionism. Herzl was born in Pest (today the eastern half of Budapest, then a separate city) to a German-speaking family originally from Zemun (now in Serbia but then in Hungary). When Theodor was 18 his family moved to Vienna. There, he studied law, but he devoted himself almost exclusively to journalism and literature, working as a correspondent for the Neue Freie Presse in Paris, occasionally making special trips to London and Istanbul. Later, he became literary editor of Neue Freie Presse,and wrote several comedies and dramas for the Viennese stage. As a young man, Herzl was engaged in a Burschenschaft association, which strove for German unity under the motto Ehre, Freiheit, Vaterland ("Honor, Freedom, Fatherland"), and his early work did not focus on Jewish life. His work was of the feuilleton order, descriptive rather than political. In spite of his Jewish ethnicity, Herzl was an avowed atheist.As Paris correspondent for Neue Freie Presse, Herzl followed the Dreyfus Affair, a notorious anti-Semitic incident in France in which a French Jewish army captain was falsely convicted of spying for Germany. He witnessed mass rallies in Paris following the Dreyfus trial where many chanted "Death to the Jews!" Herzl came to reject his early ideas regarding Jewish emancipation and assimilation, and to believe that the Jews must remove themselves from Europe and create their own state.In June, 1895, he wrote in his diary: "In Paris, as I have said, I achieved a freer attitude toward anti-Semitism... Above all, I recognized the emptiness and futility of trying to 'combat' anti-Semitism." In Der Judenstaat he writes: "The Jewish question persists wherever Jews live in appreciable numbers. Wherever it does not exist, it is brought in together with Jewish immigrants. We are naturally drawn into those places where we are not persecuted, and our appearance there gives rise to persecution. This is the case, and will inevitably be so, everywhere, even in highly civilised countries—see, for instance, France—so long as the Jewish question is not solved on the political level. The unfortunate Jews are now carrying the seeds of anti-Semitism into England; they have already introduced it into America."From April, 1896, when the English translation of his Der Judenstaat (The State of the Jews) appeared, Herzl became the leading spokesman for Zionism. Herzl complemented his writing with practical work to promote Zionism on the international stage. He visited Istanbul in April, 1896, and was hailed at Sofia, Bulgaria, by a Jewish delegation. In London, the Maccabees group received him coldly, but he was granted the mandate of leadership from the Zionists of the East End of London. Within six months this mandate had been approved throughout Zionist Jewry, and Herzl traveled constantly to draw attention to his cause. His supporters, at first few in number, worked night and day, inspired by Herzl's example. In June of 1896, he met for the first time with the Sultan of Turkey, but the Sultan refused to cede Palestine to Zionists, saying, "if one day the Islamic State falls apart then you can have Palestine for free, but as long as I am alive I would rather have my flesh be cut up than cut out Palestine from the Muslim land."In 1897, at considerable personal expense, he founded Die Welt of Vienna and planned the First Zionist Congress in Basel. He was elected president, (a position he held until his death in 1904), and in 1898 he began a series of diplomatic initiatives intended to build support for a Jewish country. He was received by the German emperor on several occasions, was again granted an audience by the Ottoman emperor in Jerusalem, and attended The Hague Peace Conference, enjoying a warm reception by many other statesmen. In 1902–03 Herzl was invited to give evidence before the British Royal Commission on Alien Immigration. The appearance brought him into close contact with members of the British government, particularly with Joseph Chamberlain, then secretary of state for the colonies, through whom he negotiated with the Egyptian government for a charter for the settlement of the Jews in Al 'Arish, in the Sinai Peninsula, adjoining southern Palestine. On the failure of that scheme, which took him to Cairo, he received, through L. J. Greenberg, an offer (Aug., 1903) on the part of the British government to facilitate a large Jewish settlement, with autonomous government and under British suzerainty, in British East Africa. At the same time, the Zionist movement being threatened by the Russian government, he visited St. Petersburg and was received by Sergei Witte, then finance minister, and Viacheslav Plehve, minister of the interior, the latter of whom placed on record the attitude of his government toward the Zionist movement. On that occasion Herzl submitted proposals for the amelioration of the Jewish position in Russia. He published the Russian statement, and brought the British offer, commonly known as the "Uganda Project," before the Sixth Zionist Congress (Basel, August 1903), carrying the majority (295:178, 98 abstentions) with him on the question of investigating this offer, after the Russian delegation stormed out. In 1905 after investigation the Congress decided to decline the British offer and firmly committed itself to a Jewish home land in the historic Land of Israel.Herzl did not live to see the rejection of the Uganda plan; he died in Edlach, Lower Austria in 1904 of heart failure at age 44. His will stipulated that he should have the poorest-class funeral without speeches or flowers and he added, "I wish to be buried in the vault beside my father, and to lie there till the Jewish people shall take my remains to Palestine". In 1949 his remains were moved from Vienna to be reburied on Mount Herzl in Jerusalem Der Judenstaat (The Jewish State, 1896) written in German, was the book that announced the advent of Zionism to the world. It is a pamphlet-length political program. His last literary work, Altneuland (in Eng. The Old New Land), is devoted to Zionism. The author occupied his free time for three years in writing what he believed might be accomplished by 1923. It is less a novel, though the form is that of romance, than a serious forecasting of what can be done when one generation shall have passed. The keynotes of the story are the love for Zion, the insistence upon the fact that the changes in life suggested are not utopian, but are to be brought about simply by grouping all the best efforts and ideals of every race and nation; and each such effort is quoted and referred to in such a manner as to show that Altneuland ("Old-New land"), though blossoming through the skill of the Jew, will in reality be the product of the benevolent efforts of all the members of the human family. Herzl envisioned a Jewish state which combined both a modern Jewish culture with the best of the European heritage. Thus a Palace of Peace would be built in Jerusalem, arbitrating international disputes—but at the same time the Temple would be rebuilt, but on modern principles. He did not envision the Jewish inhabitants of the state being religious, but there is much respect for religion in the public sphere. Many languages are spoken—Hebrew is not the main tongue. Proponents of a Jewish cultural rebirth, such as Ahad Ha'am were critical of Altneuland. In Altneuland Herzl did not foresee any conflict between Jews and Arabs. The one Arab character in Altneuland, Reshid Bey, who is one of the leaders of the "New Society", is very grateful to his Jewish neighbors for improving the economic condition of Palestine and sees no cause for conflict. All non-Jews have equal rights, and an attempt by a fanatical rabbi to disenfranchise the non-Jewish citizens of their rights fails in the election which is the center of the main political plot of the novel. Altneuland was written primarily for the world, not for the Zionists. Herzl wanted to win over non-Jewish opinion for Zionism. In his diary he wrote that land in Palestine was to be gently expropriated from the Palestinian Arabs and they were to be worked across the border "unbemerkt" (surreptitiously), e.g. by refusing them employment. Herzl's draft of a charter for a Jewish-Ottoman Land Company (JOLC) gave the JOLC the right to obtain land in Palestine by giving its owners comparable land elsewhere in the Ottoman empire. According to Walid Khalidi this indicates Herzl's "bland assumption of the transfer of the Palestinian to make way for the immigrant colonist."The name of Tel Aviv is the title given to the Hebrew translation of Altneuland by the translator, Nahum Sokolov. This name, which comes from Ezekiel 3:15, means tell—an ancient mound formed when a town is built on its own debris for thousands of years—of spring. The name was later applied to the new town built outside of Jaffa, which went on to become the second-largest city in Israel. Nearby is Herzlia, named in honor of Herzl. Herzl's grandfathers, both of whom he knew, were more closely related to traditional Judaism than his parents, yet two of his paternal grandfather's brothers and his maternal grandmother's brother exemplify complete estrangement and rejection of Judaism on the one hand, and utter loyalty and devotion to Judaism and Eretz Israel. Herzl's paternal grandfather Simon Loeb Herzl, reportedly attended the Sephardic Zionist Rabbi Judah Alkalai's synagogue in Semlin, Serbia, and the two frequently visited. Grandfather Simon Loeb Herzl "had his hands on" one of the first copies of Alkalay's 1857 work prescribing the "return of the Jews to the Holy Land and renewed glory of Jerusalem." Contemporary scholars conclude that Herzl's own implementation of modem Zionism was undoubtedly influenced by that relationship. Herzl’s grandparents' graves in Semlin can still be visited. Alkalai himself, was witness of rebirth of Serbia from Otoman rule in early and mid 19th century and was inspired by Serbian uprising and re-creation of Serbia. Jacob Herzl (1835-1902), Theodor's father, was a highly successful businessman. Herzl's mother, Jeanette (n?e Diamant) was a handsome and wise woman. She took pride in her son, but did not have a successful relationship with her daughter-in-law. Herzl had one sister, Pauline, a year older than he was, who died suddenly on February 7, 1878 of typhus. Theodor lived with his family in a house next to the Doh?ny Street Synagogue (formerly known as Tabakgasse Synagogue) located in Belv?ros, the inner city of the historical old town of Pest, in the eastern section of Budapest. The remains of Herzl's parents and sister were re-buried on Mount Herzl in Jerusalem. In 1889 he married Julie Naschauer, daughter of a wealthy Jewish businessman in Vienna. The marriage was unhappy, although three children were born to it. Herzl had a strong attachment to his mother, who was unable to get along with his wife. These difficulties were increased by the political activities of his later years, in which his wife took little interest.All three children died tragically. Pauline suffered from mental illness and drug addiction. She died in 1930 at the age of 40, apparently of a morphine overdose. Hans, a converted Catholic, committed suicide (gunshot) the day of sister Pauline's funeral. He was 39. In 2006 the remains of Pauline and Hans were moved from Bordeaux, France, and placed alongside their father.,The youngest daughter, Trude Margarethe, (officially Margarethe, 1893-1943) married Richard Neumann. He lost his fortune in the economic depression. He was burdened by the steep costs of hospitalizing Trude, who was mentally ill, and was finding it difficult to raise the money required to send his son Stephan, 14, to a boarding school in London. After spending many years in hospitals, Trude was taken by the Nazis to Theresienstadt where she died. Her body was burned.Trude's son (Herzl's only grandchild), Stephan Theodor Neumann (1918-1946) was sent to England, 1937-1938, for his safety, as rabid Austrian anti-Semitism grew. In England, he read extensively about his grandfather. Stephan became an ardent Zionist. He was the only Herzl to be a Zionist. Anglicizing his name to Stephen Norman, during WWII, Norman enlisted in the British Army rising to the rank of Captain in the Royal Artillery. In late 1945 and early 1946, he took the opportunity to visit the British Mandate of Palestine "to see what my grandfather had started." He wrote in his diary extensively about his trip. What impressed him the most was that there was a "look of freedom" in the faces of the children, not like the sallow look of those from the concentration camps of Europe. He wrote upon leaving Palestine, "My visit to Palestine is over... It is said that to go away is to die a little. And I know that when I went away from Erez Israel, I died a little. But sure, then, to return is somehow to be reborn. And I will return." Discharged in Britain he took a minor position with a British Economic and Scientific mission in Washington, D.C. Autumn, 1946, he learned that his family had been exterminated. He became deeply depressed over the fate of his family and the seeming eternal and continuing suffering of the Jewish survivors of the Holocaust languishing in European Displaced persons camp. Unable to endure the suffering any further, he jumped from the Massachusetts Avenue Bridge in Washington, D.C. to his death. Norman was buried by the Jewish Agency in Washington, D.C. His tombstone reads simply, Stephen Theodore Norman, Captain Royal Artillery British Army, Grandson of Theodore Herzl, April 21, 1918 - November 26, 1946. Norman was the only member of Herzl's family to have been to Palestine. He loved the land and the people. A major Zionist effort is underway to return the last descendant and only Zionist in Herzl's family to be reburied with his family on Mt. Herzl on December 5, 2007BEZALEL : Bezalel Academy of Art and Design is Israel's national school of art. It is named after the Biblical figure Bezalel , who was appointed by Moses to oversee the design and construction of the Tabernacle (Exodus 35:30). It is located on Mount Scopus in Jerusalem and has 1,500 students registered in programs such as: Fine Arts, Architecture, Ceramic Design, Industrial Design, Jewelry, Photography, Visual Communication, Animation, Film, and [[Art History]] & Theory. Bezalel offers Bachelor of Fine Arts (B.F.A.), Bachelor of Architecture (B.Arch.), Bachelor of Design (B.Des.) degrees, a Master of Fine Arts in conjunction with Hebrew University, and two different Master of design (M.des) degrees The academy was founded in 1903 by Boris Schatz, and opened in 1906, but was cut off from its supporters in Europe by World War I, and closed due to financial difficulties in 1929. The academy was named "Bezalel" (Hebrew: "in God's shadow") as an illustration of God's creativity being channeled to a man of flesh and blood, providing the source of inspiration to Bezalel ben Uri in the construction of the holy ark. Many early Zionists, including Theodor Herzl, felt that Israel needed to have a national style of art combining Jewish, Middle Eastern, and European traditions. The teachers at the academy developed a distinctive school (or style) of art, known as the Bezalel school, in which artists portrayed both Biblical and Zionist subjects in a style influenced by the European jugendstil (art nouveau) and by traditional Persian and Syrian styles. Like the Wiener Werkst?tte in Vienna, William Morris firm in England, and Tiffany Studios in New York, the Bezalel School produced decorative art objects in a wide range of media: silver, leather, wood, brass and fabric. While the artists and designers were European-trained, the craftsmen who executed the works were often members of the Yemenite community, which has a long tradition of craftsanship in precious metals, and whose members had been making aliyah in small groups at least form the beginning of the nineteenth century, forming a distinctive Yeminite community in Jerusalem. Silver and goldsmithing, occupations forbidden to pious Muslims, had been traditional Jewish occupations in Yemen. Yemenite immigrants with their colorful traditional costumes were also frequent subjects of Bezalel school artists. Leading artists of the school include Meir Gur Aryeh, Ze'ev Raban, Boris Schatz, Jacob Eisenberg, Jacob Steinhardt, and Hermann Struck. The School folded because of economic difficulties. It was reopened as the New Bezalel School for Arts and Crafts in 1935, attracting many of its teachers and students from Germany, many of them from the Bauhaus school which had been shut down by the Nazis. In 1969 it was converted into a state-supported institution and took its current name. It completed its relocation to the current campus in 1990. The term Bezalel school describes a group of artists who worked in Israel in the late Ottoman and British Mandate periods. It is named after the institution where they were employed, the Bezalel Academy, predecessor of today’s Bezalel Academy of Art and Design, and has been described as "a fusion of ‘oriental' art and Jugendstil." The Academy was led by Boris Schatz, who left his position as head of the Royal Academy of Arts in Sofia, Bulgaria, to make aliyah 1906 and set up an academy for Jewish arts. All of the members of the school were Zionist immigrants from Europe and the Middle East, with all the psychological and social upheaval that this implies. The school developed a distinctive style, in which artists portrayed both Biblical and Zionist subjects in a style influenced by the European jugendstil ( or art nouveau) movement, by symbolism, and by traditional Persian and Syrian artistry. Like the British Arts and Crafts Movement, Wiener Werkst?tte in Vienna, William Morris firm in England, and Tiffany Studios in New York, the Bezalel School produced decorative art objects in a wide range of media: silver, leather, wood, brass and fabric. While the artists and designers were European-trained, the craftsmen who executed the works were often members of the Yemenite community, which has a long tradition of craftsanship in precious metals, and began to make aliyah about 1880. Yemenite immigrants with their colorful traditional costumes were alsofrequent subjects of Bezalel School artists. Leading members of the school were Boris Schatz, E.M. Lilien,Ya'akov Stark, Meir Gur Arie, Ze'ev Raban, Jacob Eisenberg, Jacob Steinhardt, and Hermann Struck. The artists produced not only paintings and etchings, but objects that might be sold as Judiacaor souvenirs. In 1915, the New York Times praised the “Exquisite examples of filigree work, copper inlay, carving in ivory and in wood,” in a touring exhibit. In the metalwork Moorish patterns predominated, and the damascene work, in particular, showed both artistic feeling and skill in execution.